The Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) is an extremely restrictive diet that removes specific carbohydrates (polysaccharides, some oligosaccharides, disaccharides and polyols), and has been designed to help people with conditions such as celiac disease, chronic diarrhea, diverticulitis, cystic fibrosis, and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) like ulcerative colitis, and Crohn’s disease. Some people believe this diet helps also with SIBO and with the GI (gastrointestinal) problems that some children with autism have.
Mostly, the support and recommendations for the Specific Carbohydrate Diet come from testimonials, and there are only a few small clinical studies according to which the diet might be efficient in helping to control some gastrointestinal conditions. That has to be said that the most rigorously studied dietary therapy is Enteral Nutrition Therapy (ENT). ENT has also been accepted as a successful therapy in 80% of children.
Therefore, although the results of the early stage research show potential benefit, more research is still needed to confirm the effectiveness and safety of Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD).
Different variations of the Specific Carbohydrate Diet have been around for over 100 years. The completely grain free Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) which is low in sugar and lactose, and allows some carbs and bans others, was first developed in the 1920s by Pediatrician Sydney Haas, MD, for the treatment of celiac disease.
But in 1987, Elaine Gottschall, a biochemist, and the mother of one of Haas’s patients, published “Breaking the Vicious Cycle”, after her daughter’s IBD (inflammatory bowel disease) improved with use of the Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD). Since then the diet is more widely known (1, 3, 11).
Below you can read about the theory behind the Specific Carbohydrate Diet, in which conditions it might be beneficial, general overview how to implement SCD, and a general outline of what foods are allowed (legal) and not allowed (Illegal) on the SCD.
However, if you decide to follow this diet, you should read the book “Breaking the Vicious Cycle” which also includes recipes, and consult your doctor.
The Theory Behind The Specific Carbohydrate Diet – What is SCD and How the Diet Works?
The theory behind the Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) is that some complex carbohydrates (disaccharides (double molecules) and polysaccharides (chain molecules)) are not fully digested by your body and feed harmful bacteria in your intestines. That’s why these types of carbs are not allowed (illegal) in this diet, as giving more food to the harmful bacteria leads to their overgrowth, and increase in waste products produced by bad bacteria.
This overgrowth of harmful bacteria can set off the chain reaction or “vicious cycle,” which leads to irritation and inflammation of the intestine wall. Therefore, The Specific Carbohydrate Diet is intended to work by starving out these bad bacteria, and rescue the balance of bacteria in your gut.
The only carbohydrates you can eat in this diet are monosaccharides that have a single molecule structure that allows them to be easily absorbed by the intestine wall.
According to the theory, over millions of years people have evolved to eat predominately fish, meat, eggs, vegetables, nuts, and low-sugar fruits in contrast to the diet of nowadays (that has only been around for a mere 10,000 years) that includes grains, starches, legumes, pasta and breads.
Moreover, according to the theory, the increase in chemical additives and complex sugars in the modern diet has led to an enormous increase in health issues ranging from obesity to serious bowel disorders and brain function disorders. Therefore, the allowed foods in Specific Carbohydrate Diet are mostly those that early humans ate before the beginning of agriculture (1, 3).

Who is the Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) For? 10 Conditions in Which SCD May be Helpful
The SCD (Specific Carbohydrate Diet) is designed and mainly used to help treat people with conditions like celiac disease, diverticulitis, chronic diarrhea, cystic fibrosis, and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) such as Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis.
Some people believe this diet may also help treat SIBO, GI (gastrointestinal) problems that some children with autism have, and other autism symptoms. However, more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness and safety (3, 6).
Proponents of SCD believe this diet may be a natural therapy for numerous conditions described below.
1. Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) For IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
According to one study, the Specific Carbohydrate Diet has been shown to be effective for the treatment of IBS (irritable bowel syndrome), which is a chronic long-term disorder that causes symptoms such as bloating, gas, cramping, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, or sometimes even both.
However, for IBS, the low FODMAP diet might be a better choice as the low FODMAP diet has been clinically proven for the treatment of IBS (8).
2. Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) For SIBO (Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth)
Often people who suffer from IBS also suffer from SIBO (sometimes also called blind loop syndrome). This happens when there is an anomalous increase in the general bacterial population in the small intestine (especially types of bacteria that are usually not found in that part of the digestive tract).
Reducing or eliminating certain foods from the daily menu may improve digestive health in these people (6).
3. Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) For Candida Overgrowth
Some people use the SCD (as well as the GAPS diet), or some other typical Candida diet to treat yeast overgrowth. However, according to Chris Kresser the problem with GAPS, SCD and Candida diets (depending on how they’re done) is that these may be exceptionally low-carb diets or extremely low in glucose or sugar.
But extra low-carb diets, and diets that remove every possible source of glucose or sugar in the diet – may become ketogenic. In other words, your body starts producing ketones. This is bad because there are studies according to which Candida and other yeast can actually thrive on ketones.
There are also studies, according to which white blood cells (neutrophils), are less able to kill Candida when ketones are present. That’s why some individuals are using a low FODMAP diet for Candida overgrowth, as it seems that the bacterial markers and the fungal markers are changing and going away when implementing this diet (5).
4. Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) For Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis happens when one or more of the small bulges or pouches (diverticula) that can develop in the lining of your intestines as you get older – become inflamed, and in some cases infected. These pouches usually aren’t harmful and can occur anywhere in your intestines (called diverticulosis).
However, the inflammation or infection of these pouches (diverticulitis) can cause serious abdominal pain, nausea, fever, and a noticeable change in your bowel habits. Luckily, according to some sources – SCD diet may help in the treatment of diverticulitis (7).
5. Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) For Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is an autoimmune disorder, a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) which is an umbrella term that represents two conditions (Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis) that cause inflammation in the lining of the intestinal wall. Each type of IBD affects a different part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
Crohn’s disease may influence any part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, from the mouth to the anus. This chronic disease causes inflammation of the digestive tract, which can involve different areas of the digestive tract in different people, and lead to malnutrition, abdominal pain, fatigue, severe diarrhea, and weight loss.
Crohn’s disease can be weakening as well as painful, and it may sometimes lead to life-threatening complications (6, 7).
6. Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) For Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is also an autoimmune disorder, the second type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes inflammation and ulcers (sores) in your digestive tract. Ulcerative colitis influences only the lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum. This disorder can be debilitating and can sometimes cause life-threatening complications.
Fortunately, according to some sources, SCD may help treat people with inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis (6, 7).
7. Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) For Celiac Disease
Individuals with celiac disease can’t eat gluten (a protein found in wheat, rye, barley and other grain products). Because, if they do so, and the gluten is in the small intestine, the immune system responds by attacking the small intestine, and causes inflammation and damage to this part of the gastrointestinal tract.
Celiac disease affects only about 1% of people in the United States. So, any gluten intolerance does not mean you have Celiac disease. Celiac disease can cause symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss, diarrhea, bloating and gas, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, and constipation.
Therefore, it’s only logical that removing all grains from your diet, as in Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) may help relieve symptoms of Celiac disease (7).
8. Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) For Chronic Diarrhea
Chronic diarrhea is diarrhea that lasts for more than 2-4 weeks. For some people who have a weakened immune system, chronic diarrhea may become a serious health problem and be therefore a life-threatening illness.
However, according to the proponents of SCD, it might be an effective treatment for chronic diarrhea as well (10).
9. Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) For Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is an inherited disorder that affects the cells that produce sweat, mucus and digestive juices and causes serious damage to the digestive system, lungs and other organs in the body.
Although more research is needed to be sure if the SCD may affect cystic fibrosis (or any other condition), its proponents believe that it may be an efficient therapy for this disorder (7, 9).
10. Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Autism spectrum disorder or autism (ASD), which affects affects an estimated 1 in 54 children in the US today, refers to a wide range of developmental disabilities characterized by:
- Repetitive behaviors such as:
- Repeating words or phrases
- Repetitive movements
- Behavioral disturbances
- Challenges with social communication such as:
- Inappropriate social interaction
- Problems with social interaction
- Social withdrawal
- Unusual reactions in social settings
- Lack of understanding social cues
- Challenges with nonverbal communication
- Not engaging in play with peers
- Problems with two-way conversation
- Abnormal facial expressions or body posturing
- Poor eye contact or avoidance of eye contact
- Challenges with speech such as:
- Abnormal tone of voice
- Deficits in language comprehension
- Delay in learning to speak
- Monotonous or flat speech
- Using odd words or phrases
- Intense focus on one topic
- Lack of empathy
- Learning difficulty or disability
- Preoccupation with specific topics
- Self-abusive behaviors
- problems with sleep (12).
However, according to some people – following the Specific Carbohydrate Diet may have a positive effect on autism treatment (3).
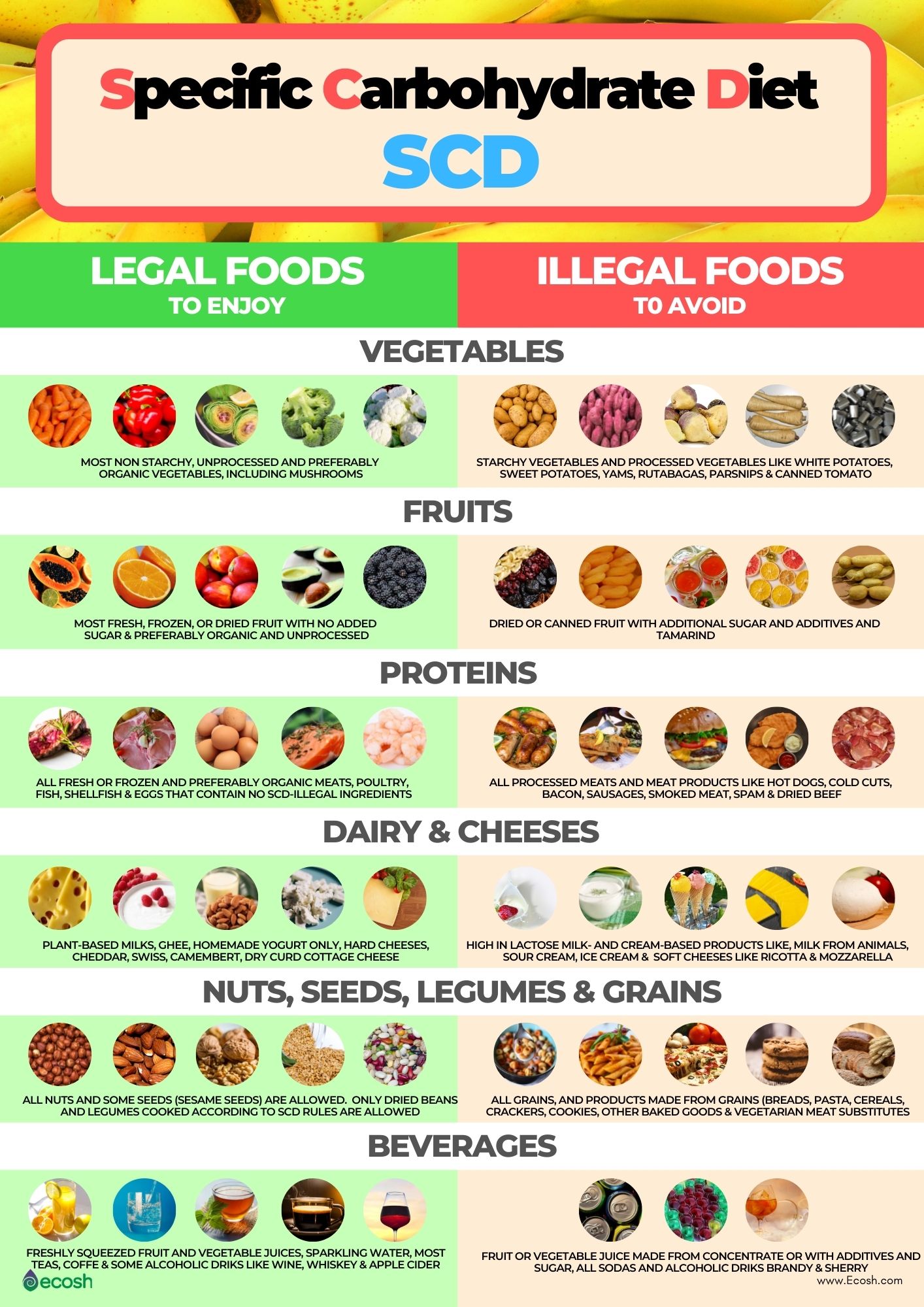
SCD Foods – What Do You Eat on a Specific Carbohydrate Diet?
Legal (Allowed) Foods in Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD)
Hereby you see a universal list of foods that are allowed (legal) on the SCD diet. If you want to find out about each allowed and restricted food in more detail, visit Breaking the Vicious Cycle website.
Fruits: Most fresh, frozen, or dried fruit with no added sugar. Preferably organic and unprocessed. For example:
- Nectarines
- Avocadoes
Vegetables: The majority of non starchy, unprocessed and preferably organic vegetables, including mushrooms. For example:
- Artichokes (French)
- Asparagus
- Bok Choy
- Broccoli
- Brussel sprouts
- Cabbage
- Carrots
- Cauliflower
- Paprika
Meats: All fresh or frozen and preferably organic meats that contain no SCD-illegal ingredients are allowed. For example:
- Beef
- Pork
- Lamb
- Buffalo
- Goat
- Venison
- Wild game
- Rabbit
- Veal
- Liver
- Kidney
- Oxtail
- Tongue
- Tripe
Poultry: All fresh or frozen and preferably organic poultry without SCD-illegal ingredients are allowed. For example:
- Turkey
- Chicken
- Guail
- Duck
- Goose
Fish and shellfish: All fresh and frozen fish and shellfish (unprocessed and without any additives) are allowed. For example:
- Anchovies
- Canned tuna (packed in water or in its own juices)
- Sashimi (but not sushi rice)
Eggs: All types of eggs are allowed, preferably free-range and organic.
Milk, yogurt, cream and butter: Allowed milk products include:
Plant-based milks, such as almond and coconut milk
- Ghee, pastured-cow or “grass-fed” butter
- Homemade yogurt only (fermented for at least 24 hours) made from cow and goat milks, coconut milk, and nut milks
Cheese: Some cheeses are allowed. For example:
- Hard cheeses aged over 90 days
- Cheddar
- Colby
- Swiss
- Camembert
- Dry curd cottage cheese
Seeds: Based on the SCD stages, and after 3 months of no symptoms, some seeds are generally allowed. For instance:
- Pumpkin seeds
Nuts: All nuts are allowed, including:
- Almonds
- Walnuts
- Pecans
- Raw cashews
- Hazelnuts
- Macadamias
- Peanuts
- All-natural peanut butter (however, all-natural nut butters may be better tolerated during initial stages)
- Coconuts and coconut milk
Beans and legumes: Only dried beans and legumes cooked according to SCD rules are allowed. For example:
- Navy beans
- Lima beans
- Black beans
- Cranberry beans
- Green (string) beans
- Lentils
- Split peas
- Regular peas
Herbs, spices and seasoning: As individual herbs and spices are allowed, you should buy your spices separately. For example:
- Basil
- Thyme
- Sage
- Parsley
- Onion powder and garlic powder (only if it is additive free)
- Salt
Condiments, dressings and vinegars: All homemade condiments, dressings and most vinegars (except balsamic vinegar ) without SCD-illegal foods are allowed. You can find recipes online and in specialized cookbooks
Sweeteners: Allowed sweeteners include:
- Honey
- Saccharine
Fats and oils: Legal fats and oils include:
- Ghee
- Pastured-cow or “grass-fed” butter
- Oils such as coconut oil, sunflower oil, and olive oil
- All seed and nut oils such as sesame oil (but not sesame seeds), peanut oil, canola oil, flaxseed oil (but not flaxseeds), corn oil and grapeseed oil
Fermented foods: Only fermented foods made without SCD-illegal foods or added sugar are allowed. For example:
- Sauerkraut
- Kimchi
- Pickles
- Other fermented foods
Binders, thickeners, additives and other: The legal ones include:
- Baking soda (not powder)
- Unflavored gelatin
- Cellulose (in supplements only)
Beverages: Legal beverages include:
- Freshly squeezed fruit and vegetable juices
- Sparkling water
- Most teas and coffee
Alcoholic beverages: Some alcoholic beverages are allowed, for example:

Illegal (Not Allowed) Foods in Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD)
Hereby you see a universal list of foods that are not allowed (illegal) on the SCD diet. If you want to find out about each allowed and restricted food in more detail, visit Breaking the Vicious Cycle website.
Fruits: Illegal fruits include:
- Dried or canned fruit with additional sugar and additives
- Tamarind
Vegetables: Illegal vegetables include starchy vegetables and processed vegetables such as for instance:
- White potatoes
- Sweet potatoes
- Yams
- Rutabagas
- Parsnips
- All vegetables that are processed with additional additives and sugar
- Canned or processed tomatoes or tomato products.
Meats: Illegal meats include all processed meats and meat products. For example:
- Hot dogs
- Cold cuts
- Bacon
- Sausages
- Smoked meats
- Spam
- Dried beef
- In addition, all meats with additional additives and sugar, including solutions
Poultry: Illegal poultry includes:
- All breaded and processed products, such as chicken nuggets and canned products
- Any poultry processed with additional additives and sugar, including solutions.
Fish and shellfish: Illegal fish and seafood includes:
- All seafood that is processed with additional sugar and additives and sugar, including solutions.
- Breaded fish and seafood
Milk, cream and butter: Not allowed foods include high in lactose milk- and cream-based products such as:
- Milk from animals
- Mild cheddar
- Store-bought yogurt (homemade yogurt is okay)
- Kefir
- Cream
- Margarine
- Sour cream
- Ice cream
Cheese: Not allowed cheeses include soft cheeses (except dry curd cottage cheese (DCCC)) such as:
- Ricotta
- Goat cheese
- Feta
- Cream cheese
- Mozzarella
- In addition, other soft cheeses
Grains, breads and cereals: Illegal grains include all grains, and all products made from grains (breads, pasta, cereals, crackers, cookies, other baked goods, and numerous vegetarian meat substitutes) such as:
- Wheat
- Spelt
- Buckwheat
- Barley
- Rye
- Oats
- Rice
- Corn
- Quinoa
- Millet
- Amaranth
- Teff
- Triticale
Seeds: Not allowed seeds include:
- Flaxseeds
- Sesame seeds
- Chia seeds
- Hemp seeds
Nuts: Not allowed nuts include nuts with an SCD-illegal starch coating or that possibly has not allowed ingredients used in the roasting process (as most commercial mixed nuts).
Beans and lentils: Illegal beans include:
- Garbanzo beans
- Pinto beans
- All canned beans and lentils
- Soy and soy products in all forms
Herbs and spices: Not allowed herbs and spices include all spice mixtures
Condiments, dressings and vinegars: Illegal ones include:
- All commercial condiments
- All commercial dressings
- Balsamic vinegar (except homemade)
- Sweeteners: Illegal sweeteners include most sweeteners except honey such as:
- Agave
- Stevia
- Cane sugar (including raw, brown, white, or rapadura)
- Molasses
- Coconut, date or other palm sugar.
- Fructose, glucose, dextrose, sucrose, and isoglucose.
- Maple
- Corn syrup
- Artificial sweeteners except Sweet’N Low (saccharine is legal, but it is possibly unhealthy)
Fats and oils: Illegal fats and oils include:
- Soybean oil
- Vegan butter products
Fermented foods: Not allowed fermented foods include all commercial products with sugar, additives, preservatives, and other SCD-illegal foods.
Beverages: Illegal beverages include:
- Fruit or vegetable juice made from concentrate or with additives and sugar
- All sodas
Alcoholic beverages: Illegal alcoholic drinks include:
- Brandy
- Sherry
Sweets and chewing gum: Illegal sweets and chewing gums include:
- All candy (except homemade candy with pure honey)
- All chewing gum
- Chocolate
- Carob
- Licorice
- Marshmallows
Binders, thickeners, additives and other: Illegal products include:
- All preservatives
- Potato flour
- Rice flour
- Sorghum flour
- Sago starch
- Tapioca
- Baker’s yeast and baking powder
- Cellulose gum
- Agar
- Carrageenan guar gum
- Whey powder, FOS (fructooligosaccharides)
- Algae (such as spirulina and chlorella) and seaweed or seaweed products
- Arrowroot
- Cornstarch
- Cream of tartar
- Dextrose
- Hydrolyzed protein
- Mastic gum
- Natural flavors
- Pectin
- Postum
- Xanthan gum (2, 3).

What You Need to Know Before Starting The Specific Carbohydrate Diet
- Firstly, as the diet requires knowledge, as well as your full adherence and commitment, you should not implement this diet without first reading the book “Breaking the Vicious Cycle“. In addition, before starting the diet, consult your doctor or dietician to make sure you’ll get all the nutrients and calories you need.
- Also, for people who are just starting SCD and especially in the first step (the anti-inflammatory step), close follow-up is needed on a regular basis. So consult with your healthcare provider in 1 to 2 weeks.
- If some food listed in the diet is known to cause you serious problems, or in worst cases an anaphylactic reaction, remove it from the diet for good. In addition, if, in the past, certain legal foods did not agree with you, remove them from your diet for a short time (about one week), and try again later in small quantities. If, after a week of removing it, a food still continues to cause issues, do not include it in the diet.
- Remember, it is strongly recommended that you eat nothing other than those foods listed as Legal on the Legal/Illegal list (Chapter 9 of Breaking the Vicious Cycle), as it is sometimes hard in practice to recognize the existence of carbohydrates in various foods.
- Keep a food journal and write down what you eat each day and how it makes you feel. This way you monitor your progress and notice links between foods and symptoms.
If your symptoms completely stop after following the diet, you may gradually come off the diet without becoming sick again. However, some people may have to remain on the diet indefinitely. The author of the Breaking the Vicious Cycle recommends remaining on the diet until at least 1 year after the last symptom has disappeared (1, 11, 13).

The Specific Carbohydrate Diet Step 1: The Intro Diet – Diet Introduction and Anti-Inflammatory Step (2-5 Days)
- According book, Breaking the Vicious Cycle, it is suggested to start with Step 1 – an introductory period of 2 days (when your symptoms such as cramping and diarrhea are not severe) to 5 days (when symptoms such as cramping and diarrhea are severe). However, most often, step 1 is followed for just 1 to 2 days. During this step you only eat a few specific foods. After the introduction diet, you can slowly move on to the regular SCD diet, meaning you can gradually add solid foods back into your diet.
- Be aware that your stool color may change during the course of the introductory diet. Also, slight increase in abdominal discomfort may occur (which is usually milder than the GI symptoms from an individual’s IBD itself). This happens most likely because the “bad” bacteria dying off, so that you can begin to heal.
- When cramping and diarrhea ease up, you can try very ripe bananas (must have brown spots), cooked fruit and cooked vegetables. If it seems that these foods cause extra gas or diarrhea, delay their consumption until later (1, 11, 13).
Step 1 Foods
Drinks:
- Diluted fruit juice from allowed fruits only (100% juice with no sweeteners or additives) such as homemade pressed apple cider (non-alcoholic cider only, brown, refrigerated) or grape juice (100% grape, any color, not frozen, not with calcium). To make juice, mix 1/2 of pressed juice with 1/2 of water. See, SCD™ Legal / Illegal List for more information about legal juices.
Breakfast, lunch and dinner:
- Homemade SCD cultured yogurt and yogurt smoothies. You can make yogurt and yogurt smoothies. Later in the diet you can add very ripe bananas (must have brown spots) and also add cooked berries into your yogurt. If you are lactose intolerant or dairy products are an issue for you, use almond milk or coconut milk to make homemade yogurt.
- Homemade broths and soups, such as chicken broth, turkey broth and beef-bone broth (as no commercial SCD-legal bone broth exists).
- Broiled beef patty or broiled fish.
- Broiled meat and vegetable patties. Only vegetable allowed in the introduction diet is carrots. Later in the diet you can make meat patties with other vegetables. For example, you can combine one part of cooked chicken (or other SCD legal meat or fish) with two parts of cooked green vegetables to make these patties.
- Dry curd cottage cheese which you can moisten with homemade yogurt. If you cannot obtain dry curd cottage cheese, substitute the drained homemade yoghurt.
- Eggs (boiled, poached, or scrambled). However, avoid eggs if your diarrhea is very severe and if you are sensitive to eggs. So add eggs with caution, after a day, particularly at the beginning of the diet. However, if you can tolerate eggs, later these can be a versatile base ingredient for pancakes and other dishes such as for example:
- Vegetables (mashed) and eggs for savory pancakes
- Chicken (mashed) and eggs for chicken pancakes
- Banana (mashed) and eggs for sweet pancakes
- Egg-drop soup from chicken broth and whipped eggs
Desserts:
- Homemade gelatin dessert. You can also use the diluted fruit juice to make homemade gelatin dessert (with plain, unflavored powdered gelatin and sweeteners such as honey or saccharine).
- Homemade applesauce (use peeled, and well-cooked apples). You can eat applesauce cold or warm, and add a bit of coconut oil for extra calories and honey and cinnamon to taste.
- Cheesecake that is made without a crust and with homemade yogurt or homemade cream cheese, eggs, honey, dry curd cottage cheese and a bit of vanilla extract.

The Specific Carbohydrate Diet Step 2: Foundation and Maintenance Step (3- to 4-Months)
- After the introduction diet, when the symptoms have abated, and inflammation markers are minimal or nonexistent, you can slowly move on to the diet foundation and maintenance step (regular SCD diet), which may last 3- to 4-months. In this step you can gradually add solid foods such as vegetables, fresh fruits, lentils, beans and nut flours.
- Above all, you should introduce only one new food back to your diet at a time, and a 2-day interval is an ideal (but not required) recommendation for introducing new foods. This way, you can determine whether you are able to tolerate each individual new food. Although, at the beginning SCD did not break the diet into steps, many helpful guidelines about in which order to introduce foods, exist online at resources such as www.pecanbread.com.
- For people with narrowed ileums (a common complication of Crohn’s disease, tuberculosis, and intestinal ischaemia) some foods may irritate the narrowed portions of the ileum. These aggravating foods include raw grapes, lots of raisins, celery, fruit and vegetable peels, spaghetti squash, and whole nuts (nut butter and nut flour seem to be usually okay). To find out more about obstructions and resections, see here.
- Initially with food preparation, all fruits and vegetables should be well-cooked, seeded, and peeled (11, 14).
5 Stages of Step 2
Below are the suggestions of how to introduce foods slowly and eat only well-tolerated foods. Here you can find recipes for the introduction diet and the stages (1-5) in step 2.
1. Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) Step 2 – Stage 1
- Fruits (deseeded, peeled and well cooked), such as for instance:
- Homemade applesauce
- Homemade pear sauce
- Overripe bananas with brown spots
- Vegetables (deseeded, peeled and well cooked (pureed vegetables is a perfect way to start)), such as:
- Spinach
- Zucchini (and other summer squash)
- Acorn squash
- Buttercup squash
- In addition, butternut squash
- Meats (broiled, boiled or roasted), such as for example:
- Turkey
- Chicken
- Beef
- Lean pork
- Lean game meats
- Nuts. However, if you are nut intolerant, you should avoid these:
- Homemade nut milk
- Blanched almond milk
- Pecan milk
- In addition, homemade nut milk yogurt
- Eggs:
- You can enjoy eggs any way you want

2. Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) Step 2 – Stage 2
- Fruits (deseeded, peeled and well cooked) such as for example:
- Apricot
- Avocado (cooked)
- Peach
- Pineapple
- Plum
- Raw avocado
- Vegetables (deseeded, peeled and well cooked) like:
- Cucumber
- Garlic
- Green beans
- Artichoke-french
- Asparagus
- Mushroom
- Pumpkin
- Other winter squash varieties (excluding spaghetti squash)
- Watercress
- Tomato
- In addition, peppers
- Meats (broiled, boiled, roasted and baked) such as for example:
- Turkey
- Chicken
- Beef
- Lean pork
- Lean game meats
- Nuts (if tolerant) such as for instance:
- Nut butters
- Homemade nut milk
- Blanched almond
- Pecan
- Coconut milk
- Blanched cashew milk
- Blanched hazelnut milk
- In addition, macadamia nut milk
- Eggs:
- You can enjoy eggs any way you want

3. Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) Step 2 – Stage 3
- Fruits (deseeded, peeled and well cooked) such as for instance:
- Papaya
- Passion fruit
- Strawberry
- Tangerine
- Watermelon
- Blueberry
- Blackberry
- Cantaloupe
- Cherry
- Date
- Elderberry
- Fig
- Gooseberry
- Grapefruit kiwi kumquat
- Lemon
- Lime
- Mango
- Orange
- In addition, raisins and dried fruits (soft and well cooked in water. However, eat raisins with extreme caution, as these are more advanced food)
- Vegetables (peeled if suitable, and well cooked) such as for example:
- Beet
- Bok choy
- Broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- Cabbage
- Cauliflower
- Celeriac
- Celery*(see note)
- Chinese cabbage
- Collards
- Eggplant
- Kale
- Leek
- Lettuce
- Lima beans-fresh
- Olive
- Onion
- Parsley
- Pea
- Peppers
- Rhubarb
- Shallots
- Snow peas
- Spaghetti squash (caution with spaghetti squash)
- Sugar snap peas
- Swiss chard
- In addition, watercress
- Meats (broiled, boiled, roasted, baked and pan fried) such as for example:
- Turkey
- Chicken
- Beef
- Lean pork
- Lean game meats
- In this step, you can add crisp-fried pork or legal bacon
- Nuts if tolerant:
- Nut flour
- Pecan flour
- Blanched almond flour ( blanched almond flour and pecan flour are the easiest to digest)
- In addition, nut butters such as blanched cashew butter, blanched hazelnut butter and macadamia nut butter
- Eggs:
- You can enjoy eggs any way you want

4. Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) Step 2 – Stage 4
- Fruits (Raw, peeled). However, there might be certain fruits you cannot tolerate such as raw grapes and too much raisins. In this case, avoid these:
- Pear
- Persimmon
- Pineapple
- Pomegranate
- Plum
- Tangerine
- Tomato
- Watermelon
- Apple
- Apricot
- Avocado
- Cantaloupe
- Cherry
- Date
- Elderberry
- Fig
- Gooseberry
- Grapefruit
- Grapes (caution with grapes)
- Kiwi fruit
- Kumquat
- Lemon
- Lime
- Mango
- Orange
- Papaya
- Passion fruit
- Peach
- Vegetables (raw) such as for example:
- Bok choy
- Broccoli
- Cabbage
- Carrot
- Cauliflower
- Celeriac
- Celery
- Chinese cabbage
- Collard
- Cucumber
- Daikon radish
- Kale
- Leek
- Lettuce
- Mushroom
- Olive
- Onion
- Peppers
- Radish
- Rhubarb
- Shallots
- Snow peas
- Sugar snap peas
- Spinach
- Swiss chard
- In addition, watercress
- Meats (broiled, boiled, roasted, baked and pan fried) such as for instance:
- Turkey
- Chicken
- Beef
- Lean pork
- Lean game meats
- crisp-fried pork or legal bacon
- Now you can add battered and deep fried meats
- Nuts (only if tolerant) such as for example:
- Nut flour
- Blanched hazelnut flour
- Cashew flour
- Macadamia nut flour
- Walnut flour
- Coconut flour
- Nut pieces
- Blanched almond
- Pecan
- Shredded coconut
- Eggs:
- You can enjoy eggs any way you want
- Beans (cooked and prepared according to the book Breaking The Vicious Cycle) such as for example:
- Haricot beans
- Lentils
- Lima beans
- Navy beans
- Split peas

5. Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) Step 2 – Stage 5
- Fruits (raw) such as for instance:
- Apple
- Apricot
- Blueberry
- Blackberry
- Cherry
- Date
- Elderberry
- Fig
- Gooseberry
- Grapes
- Olive
- Peach
- Pear
- Persimmon
- Plum
- Raisin
- Strawberry
- Tomato
- In addition, dried fruits (eat all dried fruits that have not been cooked in water in restricted manner)
- Raisins (with caution)
- Vegetables (raw):
- Now you can enjoy all vegetables in any way you want
- Meats (broiled, boiled, roasted and baked) such as for example:
- Turkey
- Chicken
- Beef
- Lean pork
- Lean game meats
- Crisp-fried pork or legal bacon
- Battered and deep fried meats
- Now you can add dried jerky
- Nuts (if tolerant) such as for example:
- Whole nuts (chewed well)
- Blanched almond
- Pecan
- Blanched hazelnut
- Cashew
- Macadamia nut
- Walnut
- In addition, shredded coconut
- Eggs:
- You can enjoy eggs any way you want
- Beans (cooked and prepared according to the book Breaking The Vicious Cycle) such as for example:
- Haricot beans
- Lentils
- Lima beans
- Navy beans
- Split peas
- Black beans
- Kidney beans (14).
Specific Carbohydrate Diet Step 3: Food Reintroduction
- In step 3 of the diet you will reintroduce so-called “illegal” foods back to your diet. However, some doctors do not recommend doing that because eating illegal foods may trigger a flare of the disease.
- Usually the reintroduction phase starts after being a year on the strict SCD.
- In this step it is vital to do things extremely slowly, one step at a time, and monitor your symptoms and inflammation markers (11).
Challenges With The Specific Carbohydrate Diet
- Firstly, individuals on the SCD may develop a lack of certain nutrients, such as:
- Secondly, as this diet limits a lot of common foods and eliminates processed foods, it can be extremely difficult to stick to.
- In conclusion, due to the lack of enough calories, it might be hard for you to maintain a healthy weight when following Specific Carbohydrate Diet (1).
NB! The information provided here is for informational purposes only, so do not consider it as health care or medical diagnosis and treatment. Do not consider this information as a guarantee of the results you want to achieve. In addition, this information is not intended to replace the advice of your physician or other healthcare professional.
Even more, you should not use it to diagnose or treat a health problem. Before changing or discontinuing your existing medication, treatment, or care, or taking any dietary supplements, be sure to consult with your healthcare professional or doctor before starting any diet or program, or if you suspect you may have a medical condition.
Written by Maria-Helena Loik
Pictures: Pexels.com, Pixabay.com, Shutterstock.com
Sources:
- Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD Diet): Reviewing How It Works (webmd.com)
- Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) Legal & Illegal Foods | NiMBAL | NIMBAL Therapy | Treat IBD with Diet
- Legal/Illegal List – Breaking the Vicious Cycle
- The Stages of SCD (pecanbread.com)
- Top 4 Mistakes People Make When Treating Candida Overgrowth | RHR (chriskresser.com)
- Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD) – SIBO Center
- Saved my mom’s life. – Breaking the Vicious Cycle
- Effects of a Low FODMAP Diet and Specific Carbohydrate Diet on Symptoms and Nutritional Adequacy of Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Preliminary Results of a Single-blinded Randomized Trial (nih.gov)
- SCD: Can the Specific Carbohydrate Diet Improve Your Digestion? (healthline.com)
- Hygiene-related Diseases | Hygiene-related Diseases | Hygiene | Healthy Water | CDC
- The SCD Steps | NIMBAL Therapy | Treat IBD with Diet
- Autism: Symptoms, Signs, Causes & Treatment (medicinenet.com)
- The Intro Diet – Breaking the Vicious Cycle
- The Stages of SCD (pecanbread.com)



