Tinnitus is an annoying and lasting sound such as ringing, clicking, buzzing, or whistling in one or both ears that is not caused by any external sound source.
Symptoms and the loudness of tinnitus vary between different people and can range from a slight nuisance to an exhausting experience. Individuals with serious tinnitus may have problems sleeping, hearing, or even working.
Ear ringing is a common issue for millions of individuals, and according to studies, between 8 to 25.3% of the people in the United States suffer from it (19).
Here in this article, we write about the tinnitus symptoms, causes, risk factors, and possible treatment options that include conventional medicines, therapies, alternative medicine, lifestyle changes, herbs, and supplements.
Tinnitus Symptoms
Tinnitus is an annoying and lasting sound in one or both ears that is not caused by any external noise. Therefore, it is often called a phantom sound. The noise people hear in their ears can range from a low murmur to a high-pitched whine.
In some cases, the sound may be so loud that it interferes with the ability to concentrate and makes it difficult to understand what other people say. Ear ringing may be persistent or occasional. The sounds people with tinnitus hear may be different and include noises such as:
- Ringing
- Buzzing
- The sound of the trumpet
- Clicking
- Roaring
- Hissing
- Whistling
There Are Two Types of Tinnitus
- Subjective tinnitus is a type of ear ringing that can only be heard by the sufferer. This is the most common type of ear ringing and can be due to problems with the outer, middle, and inner ear. These are signals entering the hearing center of the brain, which the brain interprets as ringing.
- Objective tinnitus may also be audible to the attending physician using special equipment. This relatively rare type can be caused by problems with the blood vessels, the condition of the ear bones in the inner ear, or an involuntary contraction of the muscles (18).

Possible Causes and Underlying Conditions That May Lead To Tinnitus
Although there isn’t necessarily anything abnormal or serious (even simple ear blockage can create these noises) for healthy people to experience ear ringing for just a few seconds, there can also be several more serious health conditions that can cause or aggravate tinnitus.
Possible ear ringing causes include for example:
- Hearing loss caused by aging or being constantly exposed to loud noises.
- Ear canal blockage (for example dirt, earwax, or other materials that do not belong inside the ear).
- Ear infection.
- Irritation to the auditory system.
- Sinus infection.
- Emotional stress. Ear ringing is linked with a high level of emotional stress. Anxiety, depression, and insomnia are common in people with tinnitus.
- Head or neck injuries. These types of injuries mostly lead to ear ringing in only one ear.
- Medications. Some medications that may cause ear ringing include for example:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs),
- certain antibiotics,
- cancer drugs,
- water pills (diuretics),
- antimalarial drugs,
- antidepressants.
- Thyroid disease.
- Meniere’s disease (an inner ear disorder).
- Eustachian tube dysfunction (this condition can cause a feeling of fullness in your ear).
- Muscle spasms in the inner ear (which can also make your ear feel full), that are usually caused by neurologic disorders, including multiple sclerosis. However, sometimes the cause remains unknown.
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders (TMJ is the joint in front of your ears on each side of your head).
- Ear bone changes (a usually hereditary condition caused by abnormal bone growth in your middle ear).
- Acoustic neuroma (a noncancerous (benign) tumor).
- Other tumors in the brain, head, or neck.
- Heart disease.
- Disorders of the blood vessels and circulatory system, that can cause blood to circulate through your arteries and veins with more pressure, such as:
- high blood pressure,
- atherosclerosis,
- kinked or malformed blood vessels.
- Hormonal changes.
- Diabetes.
- Migraines.
- Anemia.
- Autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
- Cause remains unknown (idiopathic tinnitus)(4, 5).

Tinnitus Risk Factors
Although anyone may suffer from tinnitus, some things may raise your risk:
- Too loud sound exposure. For example from:
- heavy equipment,
- chain saws and firearms,
- portable music devices, such as MP3 players.
- working in noisy environments (construction or factory workers, soldiers, and musicians).
- Age. Aging causes the amount of functioning nerve fibers in your ears to decrease, which may probably cause hearing problems frequently linked with ringing in the ears.
- Gender. Men are at higher risk to have tinnitus.
- Alcohol and tobacco. Both – drinking and smoking increase your risk of experiencing ear ringing.
- Some health conditions. For example:
- obesity,
- high blood pressure,
- constant stress,
- cardiovascular problems,
- history of arthritis,
- head injury (5).
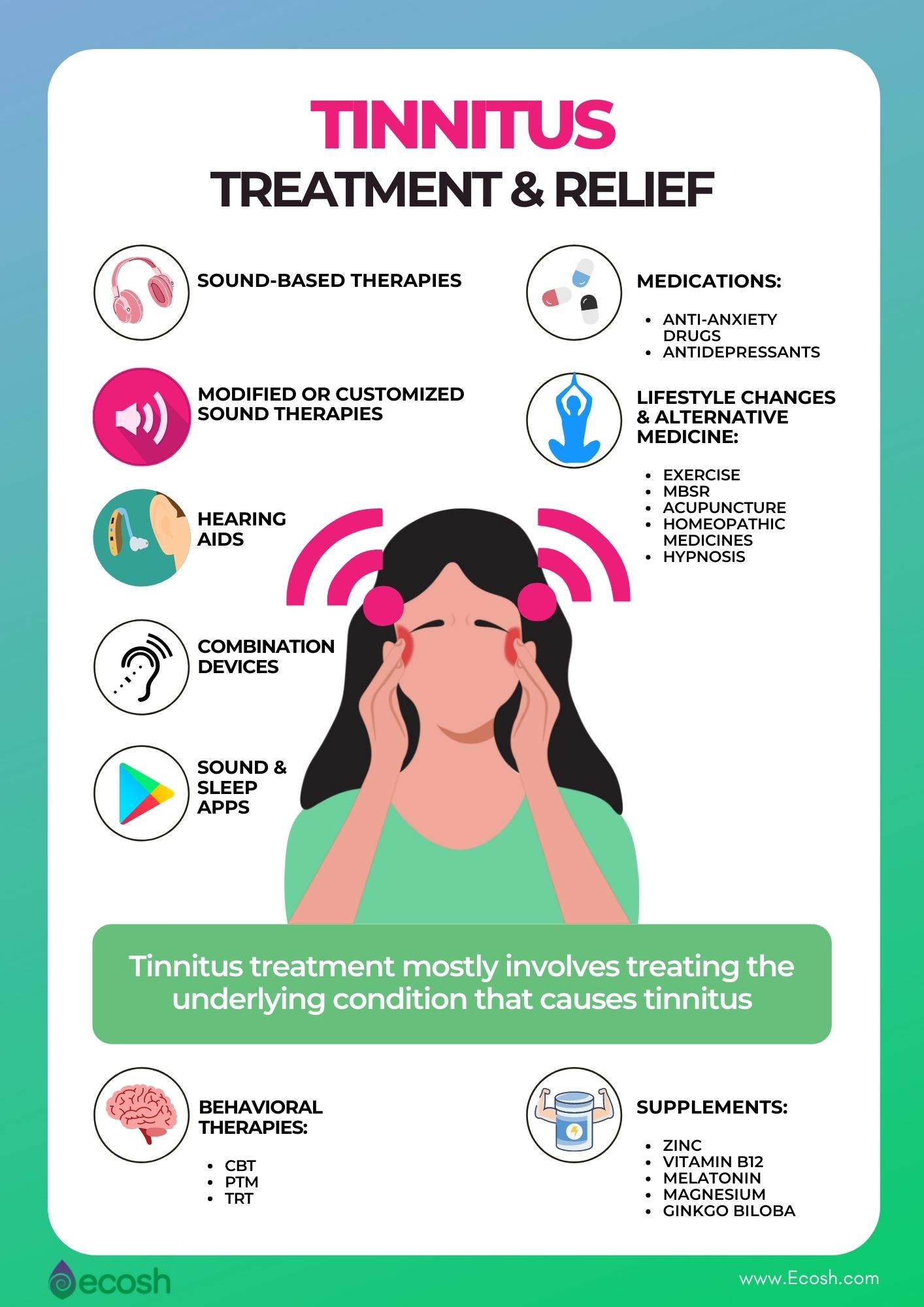
Tinnitus Treatment
The first step in tinnitus treatment is to find out the cause of it. If there is an underlying health condition, some type of dysfunction or obstruction, the treatment will first focus on curing the underlying condition that causes ear ringing. In case the cause remains unknown (idiopathic tinnitus) the treatment can focus only on reducing the intensity of tinnitus.
1. Sound-Based Therapies For Tinnitus
- Masking: provide external pleasurable sound that can help partially or completely cover the noise of ringing in the ears.
- Distraction: provide external sound to redirect persons’ focus from the noise of tinnitus.
- Habituation: help the brain recategorize tinnitus as insignificant noise, and deliberately ignore it.
- Neuromodulation: provide particular sound to reduce the neural hyperactivity which is believed to be the underlying cause (8).
Sound-masking devices for ear ringing can play music, nature noises, white noise, pink noise, or other ambient sounds. How loud someone would prefer to listen to these sounds, is up to themselves. Sometimes also other common commercial sound machines such as music, television, a fan, or regular headphones can help relax or fall asleep.
However, when it comes to sound masking, it is found that broadband noises such as white noise and pink noise are mostly more efficient than the sounds of nature (4, 9).
2. Modified Or Customized Sound Therapies
Medical-grade sound devices can provide customized sounds shaped precisely to your tinnitus. Contrary to typical sound machines, modified-sound devices are just worn sometimes, and you should be capable of witnessing relief in symptoms also when the machine is turned off. So, over some period, you may see lasting improvement in loudness of ear ringing.
In fact, researchers have found that customized sound therapy may be generally more efficient than broadband noises such as white noise at lessening tinnitus symptoms. Still, these devices can be expensive and are mostly not covered by insurance (10).
3. Hearing Aids
In most times tinnitus evolves as a sign of hearing loss because the brain goes through changes in the way it processes sounds. In this case, people may notice that the better they hear external sounds, the less they notice ear ringing. A hearing aid is a tiny gadget that increases the volume of sounds outside, and can therefore help the brain learn new methods to interpret noises (4).
4. Combination Devices (Hearing Aid Together With Sound Therapy)
There are also hearing aids that are combined with sound-making technology that ongoingly provides white noise or other customized noises. These types of gadgets unite the advantages of a hearing aid with other sound therapies and maybe therefore especially suitable for people with tinnitus and measurable hearing loss. Also, because of the portable nature of these devices, they can provide semi-continuous use and more consistent benefit throughout the day (8).
5. Free Sound And Sleep Apps
There are so many sound and sleep apps that you may find it hard to figure out the most suitable ones which might precisely relieve your symptoms or help you to sleep better. The selection of sound and sleep apps (available in Apple’s App Store and Google Play) compiled by an audiologist with tinnitus includes apps such as:
- Sound therapy:
- Sleep and relaxation:
6. Behavioral Therapies
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a kind of talk therapy that helps to identify and change negative thought patterns, and may also help people with tinnitus learn to cope with the condition (4).
- Progressive Tinnitus Management (PTM) is a treatment program offered by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). These loud noises that veterans of the armed services have come up against in war or training may frequently cause noise-induced hearing loss. Therefore, if you’re a veteran, your local VA hospital may help you find the most suitable tinnitus treatment program. Until then you can look into a step-by-step workbook offered by the National Center for Rehabilitative Auditory Research (NCRAR) at the VA (11).
- Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT) is a type of therapy that helps you to cope and live with your tinnitus on a subconscious and conscious level (10).
7. Medications
- Anti-anxiety drugs. These medications may help make your symptoms more tolerable, and thereby improve your quality of life. Some of these, like for example alprazolam (Xanax) are also associated with insomnia often linked with ringing in the ears. Anti-anxiety drugs that are commonly used for tinnitus include:
- Alprazolam (Xanax)
- Clonazepam (Klonopin)
- Diazepam (Valium)
- Lorazepam (Ativan)
- Antidepressants. Antidepressants may play a part in reducing the problem that causes ringing in the ears, not just the way you perceive it. Commonly used antidepressants for tinnitus treatment include:
- Clomipramine (Anafranil)
- Desipramine (Norpramin)
- Imipramine (Tofranil)
- Nortriptyline (Pamelor)
- Protriptyline (Vivactil) (12).
8. Lifestyle Changes, Self Help, Home Remedies, and Alternative Medicine For Tinnitus
When it comes to lessening tinnitus symptoms by yourself, there are some lifestyle changes that you can start practicing already today, and thus take a step closer to a more fulfilled and noise-free life.
- Exercise. As anxiety, depression, stress, illness, and lack of sleep all aggravate ringing in the ears, systematic and consistent exercise might help.
One good example is practicing yoga, as in addition to reducing stress, it may also lessen symptoms of subjective tinnitus (13).
- Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR). Mindfulness-based stress reduction courses may be handy in lessening your symptoms as this therapy may help people learn skills to control their attention and pull focus and thoughts away from unpleasant emotions (14).
- Alternative medicine, complementary therapies and remedies. There are various alternative treatment options for tinnitus, though non of these are backed by scientific studies just yet. Alternative treatments for tinnitus include for example:
- Acupuncture. Based on a study, acupuncture may be effective in lessening the severity and loudness of ear ringing, and can therefore be used as a good treatment option for chronic non-pulsatile tinnitus (16).
- Homeopathic medicines. Some people believe that homeopathic remedies may help those with tinnitus, as these medicines can lessen the frequency and intensity of ringing in the ears after some time (17).
- Hopi ear candles. We list these candles here not to suggest this treatment, but so you would know that there are concerns regarding this form of treatment. Besides the fact that there is no good evidence that ear candles help relieve tinnitus, the use of these has damaged some people’s ears (15).
- Hypnosis. Although there is no evidence available to demonstrate whether hypnotherapy is effective in people with tinnitus, there is some evidence that hypnosis may successfully deal with the psychological aspects of tinnitus that are linked with the causes of ear ringing, such as stress, anger, as well as anxiety. Though, hypnosis is usually more efficient when combined with other psychological therapies (4, 15).

9. Supplements For Tinnitus – Can Dietary Supplements or Herbs Help Lessen Ringing in Your Ears?
Therefore, even though some believe supplements can bring relief, you should never take a supplement to treat an auditory symptom without consulting your doctor first. That said, the listed supplements below are those usually linked with tinnitus development and the most suggested ones for tinnitus relief (1, 2).
Zinc
Zinc is an essential element that plays a vital role in the cochlear (a cavity of the inner ear that contains nerve endings crucial for hearing) and neuronal function. Thus, low blood zinc levels are associated with ringing in the ears. Meaning, that people with tinnitus often also have a zinc deficiency.
However, it does not mean that zinc supplements could be the best treatment for tinnitus in every case, but that people with zinc deficiency may see some improvement in their symptoms by taking zinc supplements (1, 6).
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is vital for circulatory and neurologic functions. For instance, too low levels of B12 may damage the vascular system and nerves of the auditory system and thus lead to hearing loss as well as tinnitus. Although more research is needed, early trials of vitamin B12 for the treatment of tinnitus show promise (1, 3).
Melatonin
Firstly, melatonin helps you to fall asleep and sleep better. Secondly, it defends against free radicals and possesses antioxidant action. Thus, although melatonin may not cure tinnitus, it may show benefits for sleep problems caused by ringing in the ears (1).
Magnesium
Magnesium is a vital mineral in numerous bodily functions, as well as hearing. Therefore, low levels of magnesium have been linked with ringing in the ears. Early studies demonstrate that magnesium supplements may probably improve ear functions, proposing that magnesium may help with how a person perceives tinnitus. Though, more research is necessary (1).
Ginkgo Biloba
Although research on Ginkgo biloba is conflicting, it possesses vascular modulator actions, improves blood flow, regulates vascular tone, and can stop blood clots from forming. As cardiovascular problems are one of the proposed causes of tinnitus, Ginkgo biloba may help those with these types of underlying causes (7).
When Should I Go To The Emergency Department (ER) For Tinnitus?
Although tinnitus is hardly ever a sign of a severe medical condition, you should consult with your doctor if you cannot hear, work or sleep normally, and go to the emergency department if you’re experiencing symptoms such as:
- Sudden hearing loss
- Facial paralysis
- Foul-smelling discharge from your ear
- A pulsating sound in your ears that is in sync with your heartbeat (4).
NB! The information provided here is for informational purposes only, so do not consider it as health care or medical diagnosis and treatment. Do not consider this information as a guarantee of the results you want to achieve. In addition, do not take this information as a replacement for the advice of your physician or other healthcare professional.
Even more, you should not use it to diagnose or treat a health problem. Before changing or discontinuing your existing medication, treatment, or care, or taking any dietary supplements, be sure to consult with your healthcare professional or doctor before starting any diet or program, or if you suspect you may have a medical condition.
Written by Maria-Helena Loik
Pictures: Pexels.com, Pixabay.com, Shutterstock.com, Ecosh.com.
Sources:
- The Truth About OTC Tinnitus “Cures” | ENT of Athens | Blog
- Common Vitamins and Supplements to Treat Ear Ringing (webmd.com)
- Therapeutic role of Vitamin B12 in patients of chronic tinnitus: A pilot study (nih.gov)
- Tinnitus: Remedies to Treat Ringing in Your Ears (healthline.com)
- Ringing in Your Ears – Symptoms, and causes – Mayo Clinic
- The role of zinc in the treatment of tinnitus – PubMed (nih.gov)
- Ginkgo biloba in the treatment of tinnitus: An updated literature review (tinnitusjournal.com)
- Sound Therapies | American Tinnitus Association (ata.org)
- Frontiers | A Mixed-Methods Trial of Broad Band Noise and Nature Sounds for Ear Ringing Therapy: Group and Individual Responses Modeled under the Adaptation Level Theory of Tinnitus | Aging Neuroscience (frontiersin.org)
- Tinnitus Retraining Therapy – What is it and how does it work? (hear-it.org)
- Progressive Tinnitus Management – National Center for Rehabilitative Auditory Research (NCRAR) (va.gov)
- Drug Therapies | American Tinnitus Association (ata.org)
- The Effects of Yoga in Patients Suffering from Subjective Tinnitus – PMC (nih.gov)
- Mindfulness-Based Therapy: New Study Underscores Tinnitus Tr… : The Hearing Journal (lww.com)
- Complementary therapies & remedies for ear ringing | British Tinnitus Association
- Acupuncture for chronic nonpulsatile tinnitus: A randomized clinical trial – PMC (nih.gov)
- Tinnitus Homeopathy Treatment, Medicines | Ring Ears Remedies & Diagnosis (homeoconsult.com)
- Eesti Tinnituse ja Meniere’i Ühing MTÜ (etmu.ee)


