Before discussing about various forms of magnesium, and why magnesium glycinate might be the best option for you, let`s make it clear why this mineral is so vital for your body at the first place. Did you know that magnesium is the second nutrient after vitamin D, which deficiency is the most common among people in developed countries?
This is very disturbing given the fact that magnesium is involved in many biochemical and enzymatic processes. Magnesium takes part in more than 300 vital enzymatic reactions, like: transmission of genetic information, absorption of vitamins and trace elements, and activation of amino acids.
It is also needed in energy production, blood pressure control, blood glucose content, and muscle and nerve function.
Experts claim that adults who consume less magnesium than their daily intake needs, are more likely to develop the symptoms of inflammation. Infections have, in turn, been associated with health conditions like heart disease, diabetes and certain types of cancer. It has also been established that there is a connection between low magnesium levels and osteoporosis.
The Causes of Magnesium Deficiency
It`s widely known, that just about 80% of people suffer from magnesium deficiency. It`s because the excessive cultivation of agricultural products and the use of pesticides have decreased magnesium content in the soil. Likewise, the foods processed in high temperatures have lost their nutritional value. So, it is hard for people to get magnesium, but easy to lose.
The causes of magnesium deficiency and why magnesium is being removed from your body:
- Stress
- Alcohol and coffee
- Eating too many sweets
- Antibiotics
- Diuretics
- Laxatives
- Cardiac assist devices
- Vitamin E deficiency
The Signs of Magnesium Deficiency
- Leg cramps and “running ants” feeling
- Tension in the body
- Twitching eyelids
- Persistent fatigue and nervousness
Moreover, dental caries, and the stagnated growth of jaw bones results in a situation where there isn’t enough space for the teeth to grow. Muscle growth and relaxation depend on magnesium.
Food Sources of Magnesium
The most beneficial and valuable organic sources of magnesium are sprouts, green leafy vegetables, wholegrain products and nuts.
For example, there is 300 mg of magnesium in:
- 60 g of cocoa powder
- 65 g of wheat bran
- 110 g of almonds
- 165 g of peanuts
- 450 g of milk chocolate
- 1.3 kg of broccoli
- 1.4 kg of leaf lettuce or romaine
- 2 kg of Chinese cabbage
How is Magnesium Related to The Nervous System
A variety of symptoms related to the nervous system can signal magnesium deficiency such as:
- Anxiety and panic attacks
- Irritability
- Agoraphobia (fear of large, open spaces and fields)
- Fatigue and exhaustion
- Headache and migraine
- Depression
- Sensitivity to bright light and loud sounds
- Restless leg syndrome
- Constipation
- High blood pressure
- Palpitations and arrhythmia
- Insomnia (a sleep disorder, which symptoms include failure to sleep without difficulties, interrupted sleep and waking up too early)
Best Types of Magnesium and Their Absorption
Choosing a magnesium supplement can be tricky due to the many different forms of magnesium (e.g., magnesium aspartate, bicarbonate, carbonate, chloride, citrate, gluconate, hydroxide, lactate, malate, orotate, oxide, taurate, magnesium threonate, and trisilicate) and wide range in recommended dosages (from less than 50 mg to over 1,000 mg). But here is a valuable universal advice for you:
Some forms, like magnesium gluconate, magnesium citrate, and magnesium lactate (glycinate), are more highly absorbable than other forms of magnesium.
For the sake of accuracy, there should be specified also other nicknames of magnesium glycinate, such as magnesium bis-glycinate, magnesium bis-glycinate-chelate, and magnesium diglycinate. All the names actually mean the same substance. It is mentioned that 1 gram of magnesium glycinate contains 10% or 100 mg of elemental magnesium.
Magnesium oxide/oxalate is the type of magnesium that has the worst absorption, as it is a very raw and cheap substance. The elemental magnesium content in magnesium oxide/oxalate is quite high at 58%, however your body is able to absorb only 4% of it.
In addition, long-term intake of magnesium oxide may clog the kidneys. Magnesium oxide causes diarrhoea. Magnesium citrate also has a light laxative effect due to the addition of citric acid in magnesium.
Which Substances Encourage The Absorption of Magnesium Glycinate?
Although magnesium can be absorbed independently, there are some vitamins and minerals that contribute to its absorption.
- Vitamin C
- The B-group vitamins (vitamin B6 in particular), because B6 helps determine, how much magnesium is absorbed into cells
- Vitamin D
- Calcium
- Potassium
- Sodium, etc.
Therefore, it is advisable to take the magnesium glycinate supplement with food so that all the other necessary substances are available. This maximize the absorption of magnesium glycinate.
Why are bioactive forms efficient? Bioactive forms have already been modified to be suitable for metabolism, and the exhausted body does not have to start using the energy to convert the passive form to active.
There is no data on magnesium overdose and according to the literature, high doses are safe, too. For example, the recommended administration of magnesium for therapeutic doses can be even as much as 800 – 3000 mg per day. Above all, the ratio of magnesium to calcium in the body should be 8:1, or at least 4:1.
The opposite ratio creates a situation where there is too much calcium in the body. But this way – without enough magnesium – calcium does not reach the bones at all and clogs the arteries and tissues. In addition, besides in the bones and muscles – your body uses magnesium for many other functions. So, the daily suggested average consumption of magnesium should be at least 375 mg.
Magnesium Glycinate is Required in The Organism for:
- The bones (approximately 70% of magnesium in the body is in the bones)
- The processing of proteins
- Releasing energy in the muscles
- Regulating heartbeats and body temperature
- The metabolism of calcium, phosphorus, potassium, zinc and sodium
- Better uptake of Vitamin C, D and E, and better absorption of B-group vitamins
- The functioning of the cardiac muscles and the control of blood circulation
- Energy release and performance of nerves and muscles
- At least 300 enzymatic reactions
- In addition, for the metabolism of carbohydrates and activating amino acids
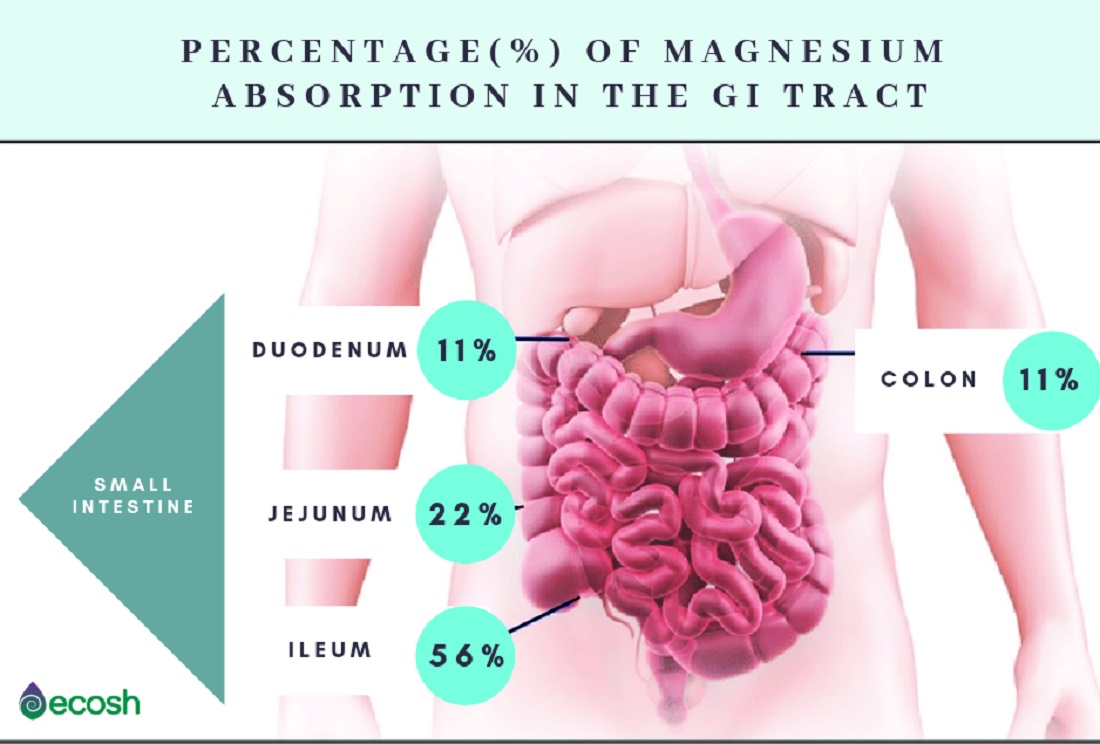
According to the studies, magnesium glycinate is very suitable for those who experiencing digestive disorders such as diarrhea or have undergone bowel resection surgery, as it absorbs well in different parts of the bowel.
Magnesium glycinate and magnesium gluconate are considered the best forms also when suffering from severe magnesium deficiency. Most importantly, as magnesium glycinate relaxes muscles and brings you good sleep, it is best to take the supplement 1h – 30min at evenings before going to bed.
How much magnesium should you consume?
The recommended daily intake of magnesium:
| 1-3 year olds | 80 mg/day |
| 4-7 year olds | 130 mg/day |
| 8-13 year olds | 240 mg/day |
| Teenagers, 14-18 year olds | boys 410 mg/day, girls 360 mg/day |
| Adults 19+ | men 400-420 mg/day, women 310-320 mg/day |
| Pregnant women | 350-360 mg/day |
| Breastfeeding mothers | 310-320 mg/day |
Compiled by Maria-Helena Loik
Sources: cbi.nlm.nih.gov, Dietvsdisease.org, Livestrong.com, Webmd.com
Pictures: Pexels.com, Pixabay.com, Shutterstock.com