Digestive enzymes are tiny helpers that aid digestion, defend your body, accelerate chemical reactions in your body, and better your health. Even more, in some cases, enzymes can make a chemical reaction millions of times faster than it would have been without it.
So, enzymes are like life keepers, as these chemical reactions that depend on the job that enzymes execute – keep us alive.
How Your Body Uses Enzymes and Why are Enzymes Important?
Heart work, breathing, thinking, maintaining the body’s internal balance and normal weight depend on enzymes. Without enzymes, nutrient digestion and uptake does not occur even in case the most rational diet. Without enzymes, nutrients cannot reach the blood, cells and tissues, and when the enzymes stop working, we simply die. For what functions do we need enzymes?
- Liver – The liver breaks down toxins in your body, and to do this job, it needs a variety of enzymes. Enzymes in the liver include: alkaline phosphatase (ALP), aspartate transaminase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT). Elevated liver enzymes (based on a blood test), designate injured or inflamed liver cells.
- Heart – Cardiac enzymes, also known as cardiac biomarkers include myoglobin, troponin and creatine kinase.
- DNA replication – Every single cell in your body holds DNA. Every time a cell divides, that DNA needs to be copied and enzymes help in this process. They unwind the DNA coils and copy the information. DNA replication requires enzymes like DNA polymerase, including DNA primase, DNA helicase, DNA ligase, and topoisomerase.
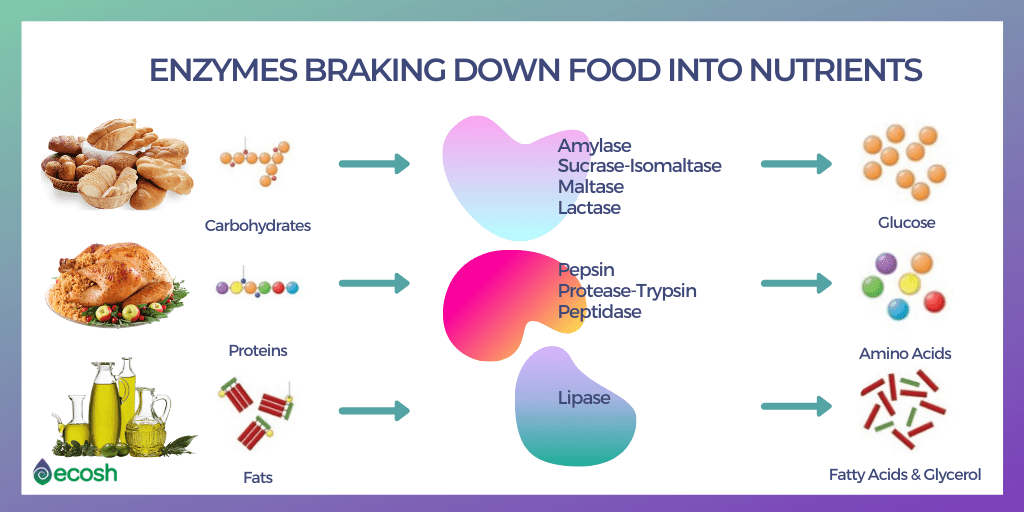
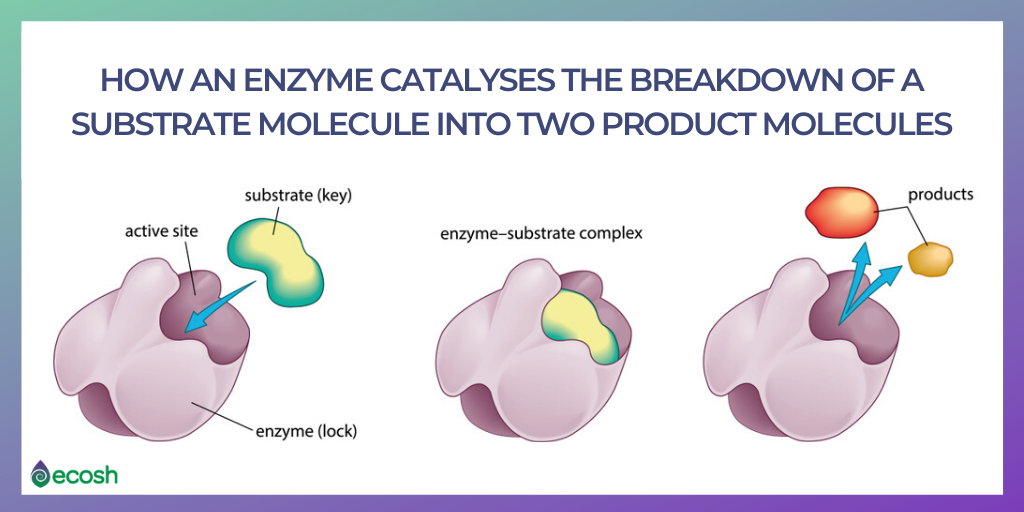
- The digestive system – Enzymes help the body to break down larger complex molecules into smaller molecules, such as glucose, so that the body can use them as fuel.
Types of Digestive Enzymes
Enzymes are both proteins and biological catalysts that regulate the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered in the process.
There are around 5000 enzymes in the body and they are classified according to the type of chemical reaction catalysed.
Digestive enzymes all belong to the hydrolase class, a group of enzymes that speed up the breakdown (hydrolysis) of food molecules into their ‘building block’ components. Another uncommon quality is that these are extracellular enzymes that blend with food as it moves through the gut.
So these proteins participate, trigger and accelerate all chemical reactions and processes in the body.
The main organs in your digestive system that produce enzymes are the stomach, pancreas, small intestine, salivary glands and liver.
Different types of digestive enzymes can break down different nutrients, for example:
- Amylase – Breaks down the carbohydrates in the oral cavity, where starch is converted to maltose (a sugar).
- Papain and Bromelain – Proteolytic enzymes derived from tropical fruits (papaya and pineapple) that hydrolyze proteins into peptides and amino acids, which in turn are necessary for the cells to have the cellular material they need to function and survive. These enzymes are also proteases.
- Protease (trypsin) – Proteases break down protein into its building blocks, including amino acids. This aids the digestion, absorption of proteins and has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Lactase – Is a plant enzyme that breaks down milk sugar – lactose to glucose and galactose.
- Lipases – An enzyme produced by the pancreas that breaks down dietary fat into glycerol and fatty acids.
- Peptidases – Synthesis amino acids from peptides.
- Sucrase – Digest sucrose (sugar) to glucose and fructose.
- Maltase – Break down maltose to glucose.
- Diastases – Break down starch into maltose.
- Invertases – Synthesis fructose and glucose from sucrose (a type of sugar).
25 Natural Sources of Digestive Enzymes
If your body is unable to make enough digestive enzymes, food molecules cannot be digested properly. This can lead to digestive disorders like for example lactose intolerance.
However, eating foods that are high in natural digestive enzymes can help improve digestion. Many potent enzymes are found in fresh plant foods such as fruits, green plants, germs, nuts, natural wine and fermented vegetables.
Foods and drinks that contain the most natural digestive enzymes
Raw Fruits and herbs
- Kiwifruit – It’s a great source of digestive enzymes, particularly a protease called actinidain. This enzyme helps digest proteins, aid digestion, reduces bloating and helps relieve constipation.
- Pineapple – Pineapples contain a group of digestive enzymes called bromelain. Bromelain is also available as a supplement and helps break down proteins into amino acids.
- Papaya – Like pineapples, papayas also contain proteases that help digest proteins. These proteases are known as papain and these break down proteins into building blocks, including amino acids. Papaya also helps in case diarrhea, constipation and reflux disease. High heat can destroy their digestive enzymes, so make sure to eat papayas ripe and uncooked.
- Mango – They contain the digestive enzymes amylases, which breaks down carbs from starch (a complex carb) into sugars like glucose and maltose. Amylase also helps mangoes ripen.
- Bananas – Bananas contain amylases and glucosidases, two groups of enzymes that break down complex carbs like starch into smaller and more easily absorbed sugars. These sugars are more active as bananas start to ripen. This is also the reason why yellow bananas are much sweeter than green banana. Bananas also help in case constipation and reflux disease.
- Ginger – Ginger contains the protease zingibain, which digests proteins into their building blocks. Even more, ginger appears to help food move faster through the stomach, boost the body’s own production of digestive enzymes, and be a promising treatment for nausea and vomiting.
- Avocados – They contain the digestive enzyme lipase, which helps digest fat molecules into smaller molecules, such as fatty acids and glycerol, which are easier for the body to absorb. Although lipase is also made by your pancreas, consuming avocados or taking a lipase supplement may ease digestion after a high-fat meal.
- Aloe Vera
- Garlic
- Coconut
- Figs
Other foods and drinks
- Honey – This delicious liquid is rich in many beneficial compounds. However, processed honey is often heated, and high heat can destroy digestive enzymes, so make sure that you’re buying raw honey if you’re seeking its digestive health benefits. Honey contains digestive enzymes like:
- Diastases – Break down starch into maltose
- Amylases – Break down starch into sugars like glucose and maltose
- Invertases – Sucrose into glucose and fructose
- Proteases – Proteins into amino acids
13. Bee pollen – Bee pollen also contains amylase and a host of other enzymes.
- Kefir – Kefir is a fermented milk beverage that contains cultures of yeast, lactic acid bacteria, acetic acid bacteria and many digestive enzymes, including lipases, proteases and lactases. These enzymes are essential, because they break down fat, protein and lactose molecules, respectively. Kefir also helps in case diarrhea, constipation and reflux disease.
- Wheatgrass juice
- Barley Grass
- Flax seeds
- Chlorella
- Spirulina
- Pau A`arco

Fermented foods
- Sauerkraut – Sauerkraut is a type of fermented cabbage that is also considered as a probiotic food and is rich in many digestive enzymes. The probiotic properties of sauerkraut may help ease digestive symptoms, such as bloating, gas, constipation, diarrhea, reflux disease and stomach pain, in both healthy adults and those with IBS, Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Kimchi – Like sauerkraut, kimchi is another dish made from fermented vegetables. It contains bacteria of the Bacillus species, which produce proteases, lipases and amylases. These enzymes separately digest fats, proteins and carbs. Kimchi also helps in case diarrhea, constipation and reflux disease.
- Soy sauce – Soy sauce which is made from fermented soybeans, water, salt, yeast and wheat is best without added coloration. It aids in the digestion of proteins and carbohydrates.
- Miso – Other good sources of digestive enzymes include miso, made from fermented soybeans, rice or barley. Because of added fungi koji, miso contains a variety of digestive enzymes, including lactases, lipases, proteases and amylases.
- Tempeh – is also a good source of digestive enzymes, made by a natural culturing and controlled fermentation of soybeans that binds them together.
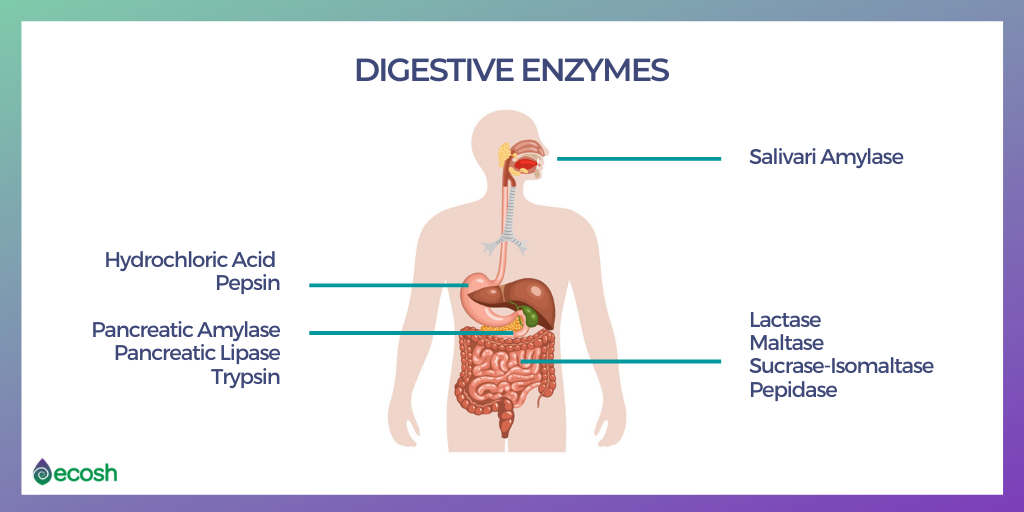
How to Boost The Work of The Digestive Enzymes?
We get enzymes from food, but our body produces enzymes also by itself. The highest amounts of enzymes are produced with saliva, then in pancreas and in our intestinal microflora. For their proper work in the body, enzymes need vitamins and minerals, especially:

What Causes Enzyme Deficiency in The Body?
Inappropriate lifestyle is the biggest factor that contributes to the destruction of enzymes. Wrong lifestyle choices include:
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Overeating
- Lack of nutrition
- Poor exercise
- Stress
- Negative emotions
- Medication
- Lack of water
Also, the pre-prepared food does not contain enzymes, it is “dead” food. Because enzymes are already destroyed by the heat treatment at 48 temperature degrees Celsius. When a person loses appetite, it is primarily about the lack of digestive enzymes in the body.
Enzymes are most active at 36-40 degrees, while raising the temperature by 0.5 degrees increases their activity by 35%. Apparently, the body raises its temperature in the event of illness to activate the enzymes to the required extent.
Enzyme Deficiency Symptoms – What Happens if You Don`t Have Enough Digestive Enzymes in Your Body?
Due to the lack of enzymes, their inadequate activity or disturbance of the microflora balance in the intestine, the body does not receive the necessary amount of nutrients to ensure the proper functioning of all body systems and organs.
If the body does not receive nutrients for its proper activity and function, then all possible diseases can develop from this base. Therefore, the lack of enzymes can lead to health problems or even stop the recovery and self-healing processes in the body.
For example, dysbacteriosis can be the cause of nine out of ten diseases. Dysbacteriosis is a disease in which the ratio of beneficial to harmful bacteria is impaired and tends to favor the harmful ones.
So, in case of dysbacteriosis, the body is not only deprived of useful substances, but is also attacked by pathogenic microflora (microbes).
Prolonged dysbacteriosis can lead to:
- Milk intolerance
- Uterine bleeding
- The development of uterine myomas
- Disorders of ovarian function
- Food allergy
- Chronic fatigue
- Obesity
- Urinary tract infections
- Kidney and bladder stones
- Various skin, liver, kidney, stomach and intestinal diseases
- Gastroesophageal Reflux disease
- Herpes
- Tonsillitis
- Bronchitis
- Asthma
- Anemia
- Diabetes
- Arthritis
- Osteoporosis
- Atherosclerosis
- Hypertension
- Premature aging
- Cancer
- Sclerosis
- Depression
- Oncological diseases

Why Should You Take Digestive Enzymes Supplements?
- To support digestion and alleviate enzyme deficiency
- In case you eat mostly processed and cooked foods
- Lactose intolerance
- Gluten intolerance
- In the absence of fresh and varied food
- In case of bowel diseases, as the body is no longer able to break down and absorb nutrients
- Chronic fatigue and exhaustion as stress destroys enzymes
- With aging, when the gut is no longer able to produce the required amount of enzymes
Administration of Digestive Enzymes
Enzymes must be consumed with each meal so that the body can also absorb all minerals, vitamins and proteins. Furthermore, it would also be very useful to take probiotics to support the digestive process and the absorption of nutrients in the intestine.
Compiled and edited by Maria-Helena Loik
Sources: Medicalnewstoday.com, Healthline.com, Ecosh.com, Wikipedia.org, Sciencelearn.org
Pictures: Pexels.com, Pixabay.com, Shutterstock.com